Unlocking the secrets of multispecies hunting

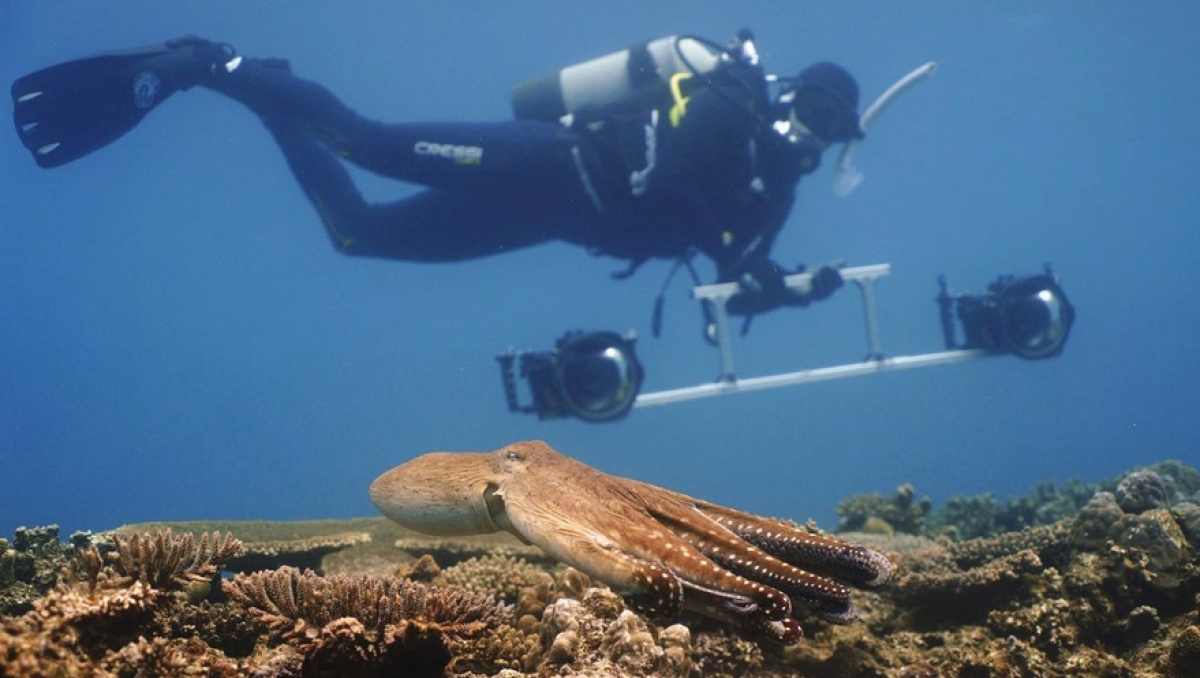
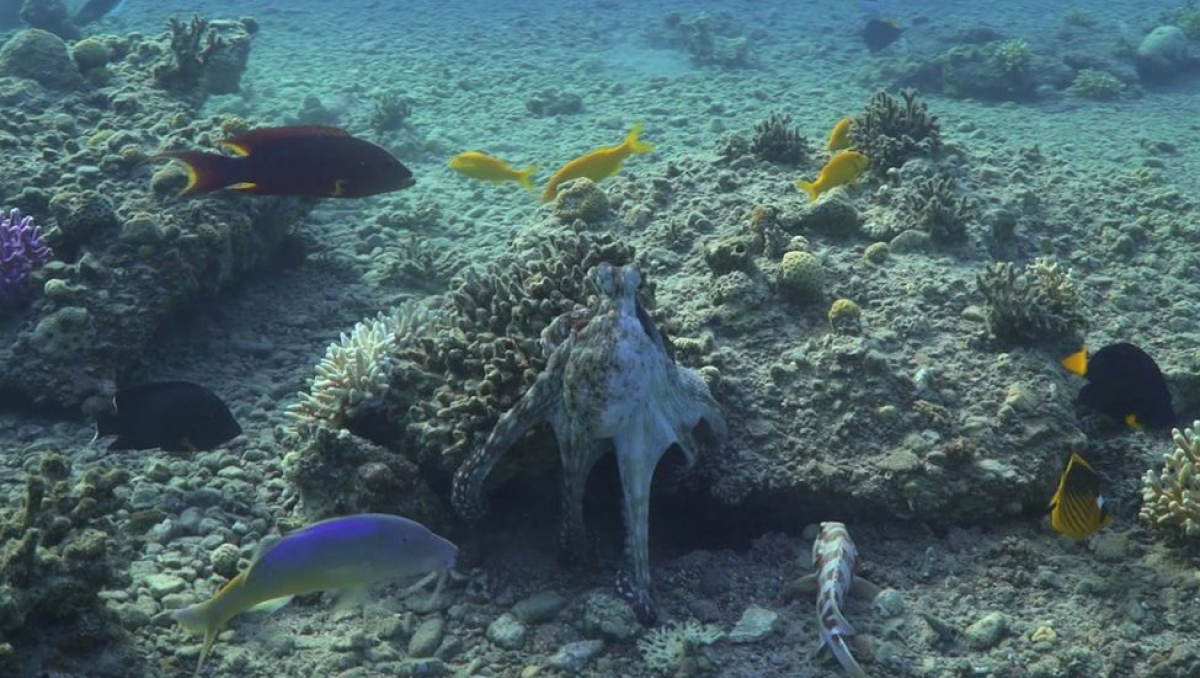
The diving gear is on, the cameras are ready – biologist Eduardo Sampaio and his colleagues are set to go. They dive in the Red Sea, scanning left and right underwater – and wonder: Where can an octopus hunting be found? Finally, they spot one. The team operates the two cameras they have with them, and station many more to collect data. Then, it’s time to wait. Months later, after analyzing more than 100 hours of film material from dives in Israel, Egypt, and Australia, Eduardo Sampaio is more than pleased with the footage. The two camera perspectives have enabled him to create a 3D view of the scene in the Red Sea – and provide him with novel insights into multispecies hunting.
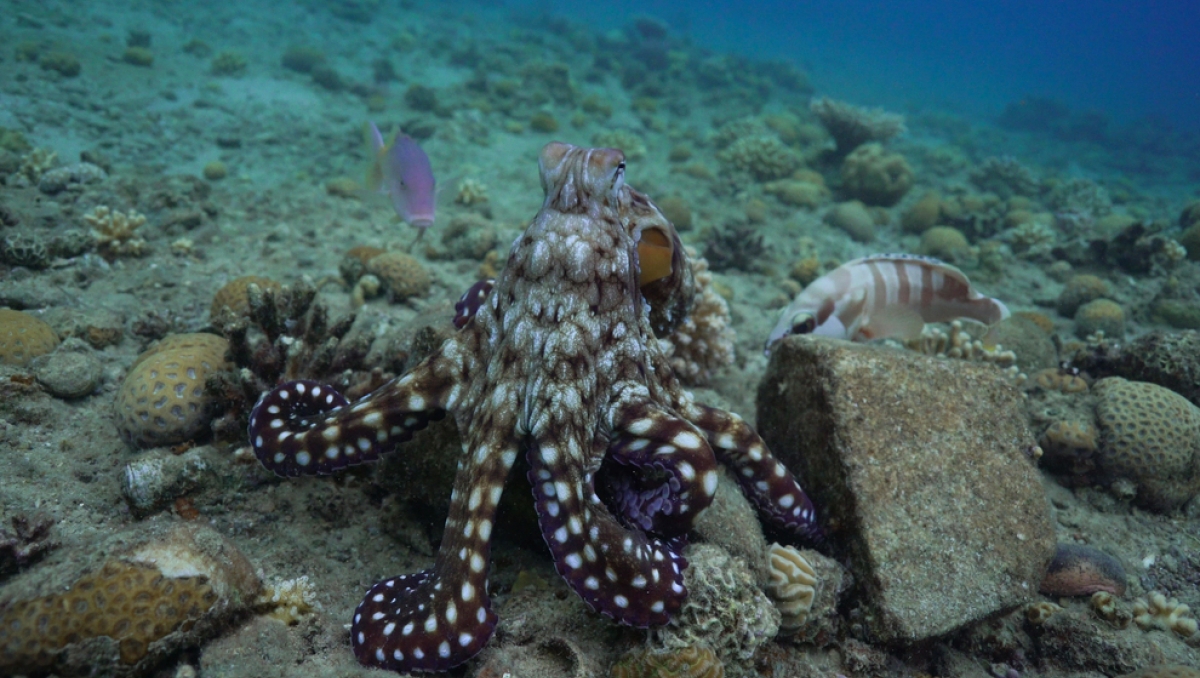
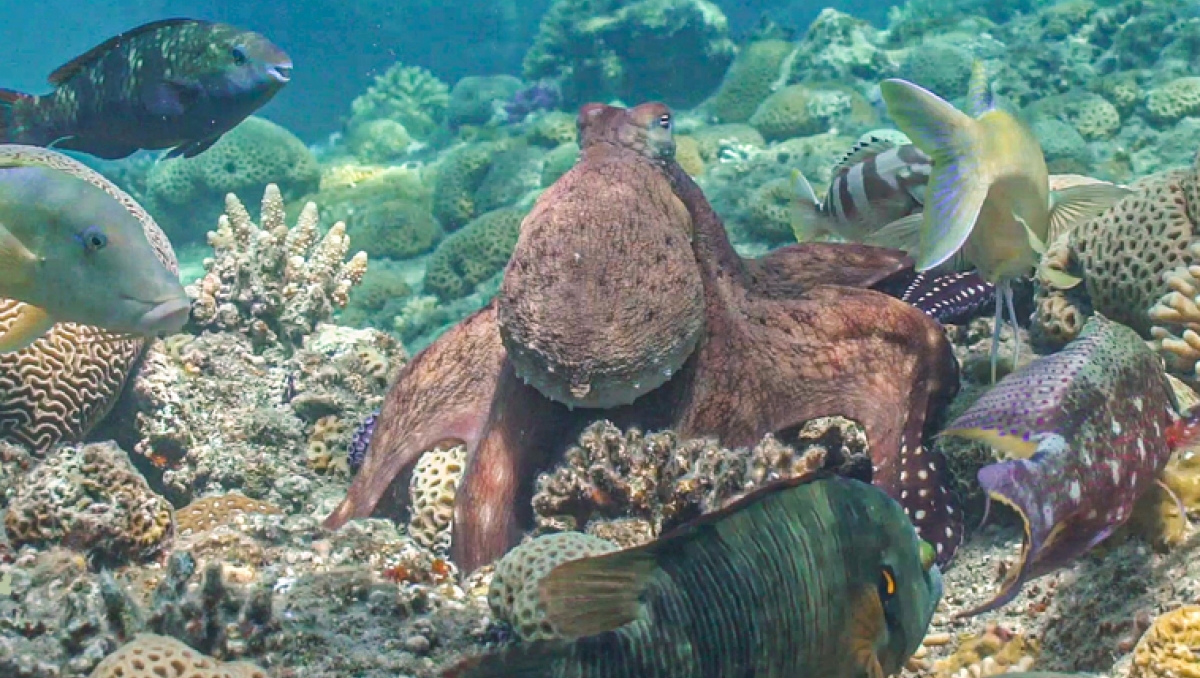
Utilizing advanced 3D field-based tracking and field experiments, Eduardo Sampaio observed that multispecies groups display unique and composition-dependent properties. “In groups of Octopus cyanea and various fish species, social influence is not evenly distributed but rather hierarchically structured across multiple dimensions, reflecting specialized roles within the group,” says the biologist. Notably, fish, particularly goatfish, are responsible for environmental exploration, dictating the group’s direction, while the octopus determines the timing and initiation of group movement.
In an intriguing display of ecological synergy, fish act as an extended sensorial system for octopuses. They are covering larger areas and enhancing prey detection efficiency.

“This beneficial interaction enables fish to acquire otherwise unreachable prey, and octopuses to conserve energy by focusing on high-quality food sources, while exerting control and providing feedback within the group, highlighting the sophisticated dynamics of marine life collaboration.”
Eduardo Sampaio
New perspective on leadership
Leadership in animal groups, be it fish, birds, or apes, is usually associated with driving the group forward. However, this study shows that leadership can emerge from both the stimulation and inhibition of movement in others, with the octopus acting as the main influencer of movement through inhibition. Moreover, the group's composition significantly influences individual investment and collective action, revealing exploitation by different group members. Such prompts partner control mechanisms, mainly by the octopus, that punches the exploiters, reinforcing its position as the de facto leader. These actions help the octopus to maintain the benefits it receives from collaborative partners.
https://youtu.be/8gCDfiZtkoo?feature=shared
In concrete terms for the hunting situation this means: “When the octopus catches the prey it also kills it”, says Eduardo Sampaio. “One item of prey is not divided, it is taken by whoever catches the prey first! However, because the interaction between the fish and octopus repeat several times during a hunt, prey is 'shared' in the sense that sometimes the octopus catches the prey, and other times fish catch the prey.”
This research demonstrates that the otherwise solitary Octopus cyanea exhibits remarkable social competence and cognitive flexibility, adapting its behaviour in response to the actions of different species. “These results broaden our understanding of leadership and sociality, emphasizing the complexity and adaptability of social interactions in nature”, summarizes Eduardo Sampaio.
Original paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-024-02525-2
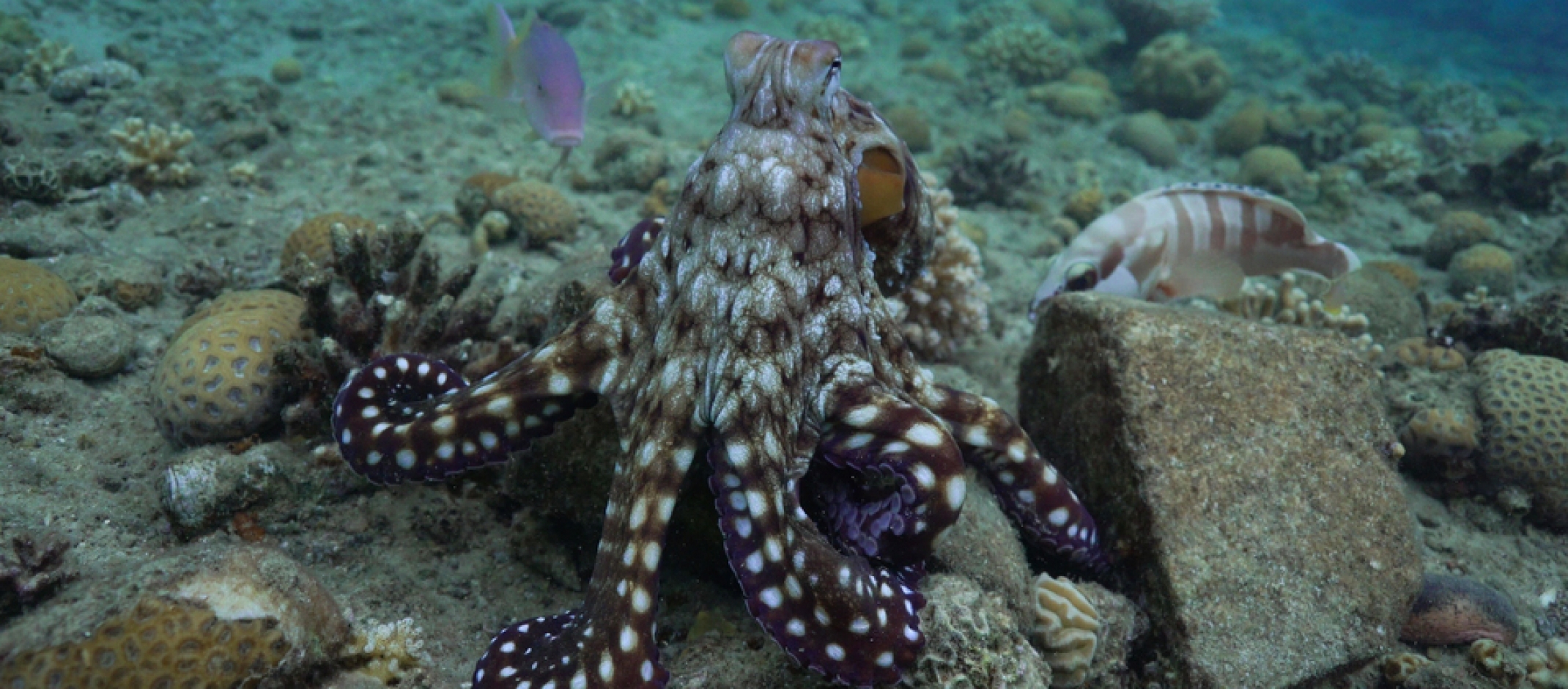
Octopus with goldsaddle goatfish
Particularly the goatfish (Mullidae) are responsible for exploring the environment. They determine the direction of the group's movement, while the octopus takes the lead, sets the timing, and initiates the group's motion. This collaboration allows the fish to access prey that would otherwise be unreachable, while the octopus conserves energy by focusing on high-quality food sources.Underwater cameras
Eduardo Sampaio and his team film with 360-degree underwater cameras that weigh ten kilograms. This allows them to capture the hunting scenes from various angles. The footage enables the scientists to create a 3D view of the hunting scene and gain deeper insights into the animals' behaviour.
Quotation image: Martim Seco